Introduction
TinyGS is a project facilitating the reception of CubeSat and the decoding of telemetry using LoRa modulation. This project is led by José (G4lile0), Spanish radio amateur. LoRa (Long Range) modulation is based on a spread spectrum transmission widely used in connected objects (IOT: Internet of Things) on 868MHz. This technology competes with Sigfox® in IOT, and is not limited in the size of the packets transmitted.
The ease of implementation and very fast, lies in the use of the TTGO ESP 32 module (433 Mhz) already described in a previous issue of Radio-REF concerning the reception of radiosondes. Indeed, these modules have a Semtech SX127x modem specially designed for connected objects.

More and more CubeSats are equipped with this type of modem or equivalent to transmit telemetry. This avoids the need to use a software « gas factory » consisting of :
- An RTL-SDR key;
- SDR reception software such as HD-SDR, SDR Sharp, etc;
- A virtual Audio bridge ;
- A software modem;
- CubeSat specific telemetry decoding software;
- Software for predicting the time of the satellite’s passage.
- Not to mention the monopolisation of a computer for 24 hours.
The TTGO ESP 32 module has the advantage of combining all the functionalities described above, but only for specific CubeSats.
For the management of the module and the reception of telemetry, José has designed a very powerful software suite. Indeed, the user can set up the module with a simple smartphone or consult the frame decoding on a dedicated WEB server. This adds great flexibility of use and promises very interesting prospects for future CubeSat launches.
The software architecture of the dedicated server :

Firmware programming in the TTGO module
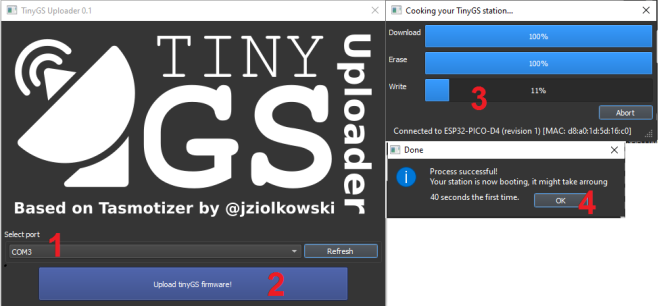
The first step is to plug the module into a computer and check for automatic driver installation. On W10, the driver should install automatically. If not, you will have to install the CP210xVCPInstaller drivers. Then download the executable file TinyGS_Uploader_WINDOWS.exe, and run it. The programming is very intuitive, you just have to select the right com port, then click on « upload ».

4 steps to program the firmware into the TTGO
Initial setting
Initially the TTGO is configured as a Wi-Fi access point. Use a smartphone to connect to the module like any other access point. In a browser enter the IP address 192.168.4.1. The home page should appear.

You now need to configure your station as shown in the image below and the online help. Be careful to put commas for the GPS location in decimal degrees. Do not forget to choose a password of 8 characters minimum. The TinyGP project must be connected to the internet to receive the various updates and automatically.

The protocol used to communicate with the TTGO module on the internet is MQTT
(Message Queuing Telemetry Transport). This protocol is very popular in connected objects. The login and password are obtained by using the telegram messaging system.
Click on open private chat :

The /mqtt command is used to obtain an MQTT login and password

The /weblogin command provides a custom URL to access the DOTT outside of the QRA

Once the configuration is complete, apply the changes and after a restart of the module, it should connect to your wifi internet access point.
Configuration and verification
Using a PC and a browser on the local network, enter the IP address of the module on the OLED display. Then click on the « station dashboard » icon
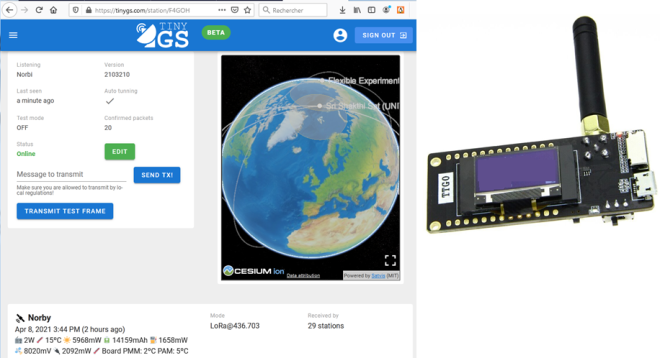
All the configuration is correct, the CubeSat Norbi was even decoded during the night :

The station should appear on the tinyGS website and on the world map.

The custom link obtained with the /weblogin command allows you to view the telemetry and select a particular satellite.
The interface is very well done, you can see the coverage areas of each satellite

Display of the last reception on the OLED screen of the TTGO
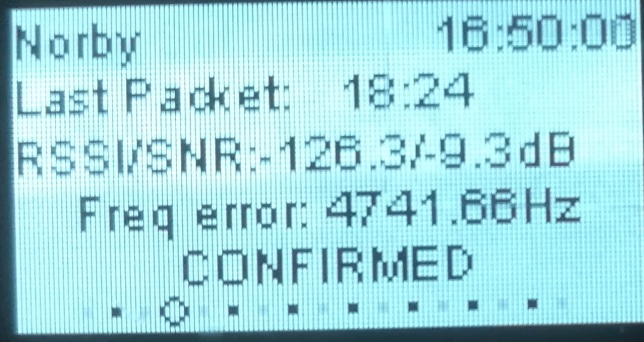
Telemetry on CubeSat Norbi

Conclusion
Receiving telemetry from CubeSats has never been easier and at a cost that does not involve any risk. A video presentation is also available on YouTube. I congratulate the whole project development team. This is a good springboard to take your first steps in satellite reception. The system works in perfect autonomy. What a pleasure it is to check the tinyGS web pages to see if a frame has been received by its module during the day or during the night. This project is in the same line as r2could described on my web page (Part 7: r2cloud and auto rx radiosonde)
73 and enjoy listening.